| Purity | 98% |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Purity Testing Method | HPLC |
| Structural Identification Method | NMR/MS |
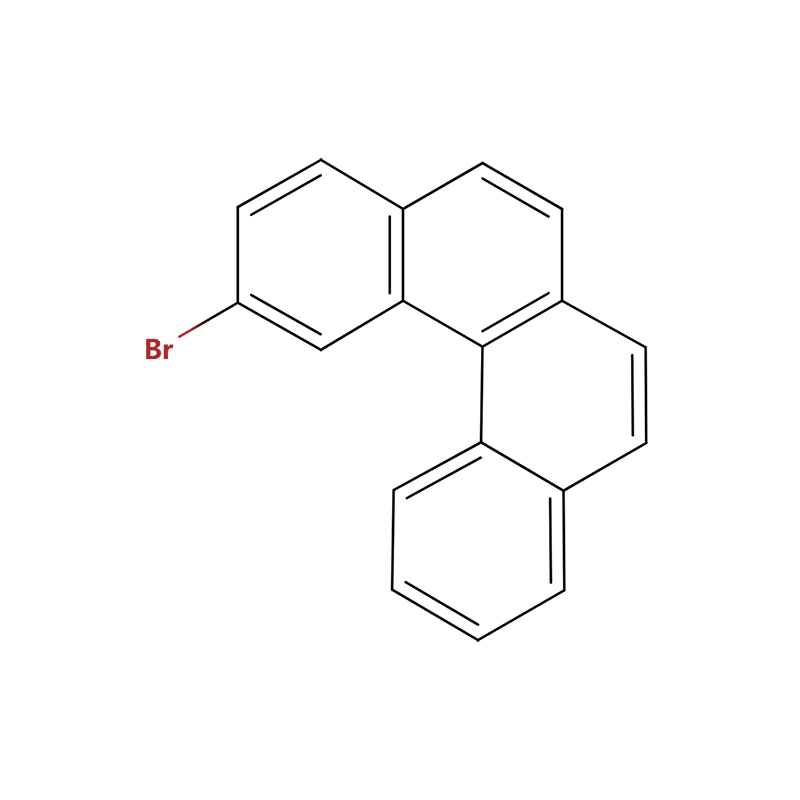
| SMILES string | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC3=C2C4=C(C=C3)C=CC(=C4)Br |
The benzo[c]phenanthrene framework, a fusion of four benzene rings, possesses an inherent helical twist due to steric repulsion between hydrogen atoms on its terminal rings. This structural feature, which classifies it as a tetrahelicene, is not merely a curiosity but a critical determinant of its properties and applications. This inherent chirality and rigid, three-dimensional architecture make benzo[c]phenanthrene and its derivatives highly valuable in the design of advanced organic materials.
In materials science, the controlled arrangement of molecules is paramount. The helical shape of the benzo[c]phenanthrene skeleton can influence the solid-state packing of materials, potentially leading to unique bulk properties. This has implications for the development of organic semiconductors, where molecular organization directly impacts charge transport efficiency. Furthermore, the chiroptical properties arising from its helical nature make it a compelling candidate for applications in circularly polarized light detection and emission, crucial for next-generation displays and optical data storage. Its derivatives have been investigated as building blocks for more complex helical structures, such as helicenes, which are explored for their use as chiral catalysts and ligands in asymmetric synthesis.
-
Symbol GHS
-
危险代码
-
风险声明
-
安全声明
-
RIDADR
-
WGK Germany
-
RTECS
-
F
-
危险性类别
-
包装等级
-
HS Code
-
毒性
-
Autoignition Temperature






 SDS
SDS COO/COA
COO/COA